In the age of precision and speed, algorithmic trading has emerged as a favored technique for traders worldwide. Here’s a step-by-step guide to crafting an effective trading algorithm.
1. Navigating the Best Market for Your Algorithm
Different markets cater to varied trading styles. Whether you’re looking at the Forex market with its continuous trading window, the stock market with its equity-focused trading, or the volatile world of cryptocurrencies, your choice should mirror your trading goals. Researching factors such as historical volatility, average traded volume, and market hours can help determine which market might be most responsive to algorithmic strategies.

2. Deciphering Symbols in Trading
Symbols, or tickers, represent specific trading instruments. These could range from ‘AAPL’ for Apple Inc. in stock markets to ‘EUR/USD’ in Forex. It’s not just about knowing these symbols but understanding their historical price movements, liquidity, and correlations with other assets. Analyzing price charts, news related to these symbols, and their market sentiment can be beneficial when deciding which symbols to target.
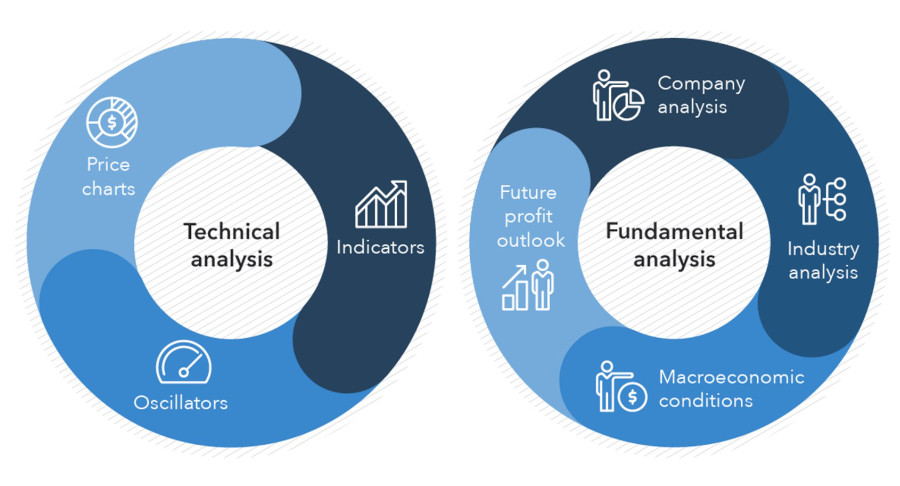
3. Identifying Market Conditions for Entry
Every market condition, be it a bullish uptrend, a bearish downtrend, or a sideway ranging market, provides unique trading opportunities. While uptrends might favor ‘buy and hold’ strategies, downtrends might require short selling techniques. Ranging markets, on the other hand, can be trickier and might require breakout strategies or oscillators to identify potential moves. Recognizing these patterns early is crucial.
4. The Intricacies of Time Intervals
Every trading strategy rests on a specific time frame. Day traders might look at 1-minute to 1-hour charts, swing traders at 4-hour to daily charts, and long-term investors might analyze weekly to monthly charts. It’s essential to understand that longer time frames often filter out market noise, but shorter ones might provide more trading opportunities. However, during backtesting, utilize the smallest possible time frame for precision.
5. Crafting the Entry Formula
The entry point is where the magic begins. While technical indicators like Moving Averages or RSI might guide some, others might rely on AI-driven predictions or news-based event trading. This formula should be dynamic, adjustable to market changes. Remember, while general strategies can work, the most effective algorithms are often tailored to specific symbols, taking into account their unique behaviors and historical data.
6. Setting Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Points
Risk management is the bedrock of successful trading. Stop-loss points ensure you limit your losses in unfavorable market movements, while take-profit points allow you to lock in profits before market conditions reverse. Defining these thresholds can be based on fixed price points, technical indicators, or a percentage of your trading capital.
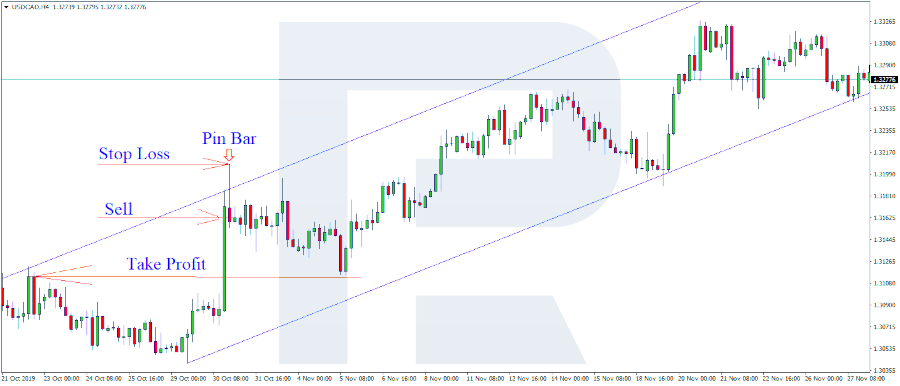
7. Defining Exit Strategies
While the primary purpose of an exit strategy is to preserve capital and lock in profits, it’s also about opportunity cost. Should your capital remain tied up in a non-performing trade, or is there a better opportunity elsewhere? Whether it’s a reversal pattern or a counter signal from your technical indicators, your algorithm should be smart enough to recognize when it’s time to exit.
8. The Importance of Backtesting
Before unleashing your algorithm, simulate its trading decisions on past market data. This exercise will provide insights into its potential profitability and risk. However, a common pitfall is over-optimizing or ‘curve-fitting’ an algorithm to past data. An over-tuned algorithm might falter in real-time trading, given the ever-changing market conditions.
9. Performance Validation Metrics
While profits and losses are straightforward metrics, delve deeper. Look at the Sharpe Ratio, which measures risk-adjusted performance. Assess the Maximum Drawdown, indicating the largest single drop from peak to bottom. Examine the Profit Factor, which compares the gross profit to the gross loss. Understanding these metrics will provide a clearer picture of algorithm performance.
10. Forward Testing: Taking Baby Steps
Starting with a demo account or trading with a minimal amount helps in gauging how the algorithm performs in real-time conditions. Once consistent results are observed, incrementally increase the trading capital.
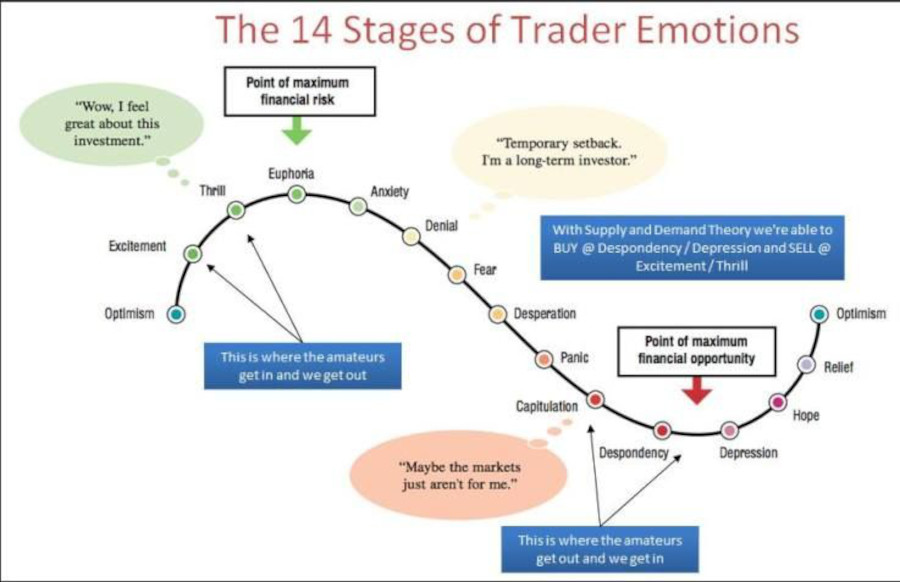
11. The Dangers of Emotional Tweaks
Trading can be an emotional rollercoaster. After a string of losses, the temptation might be high to modify the algorithm. However, rash decisions can be detrimental. Instead, set performance review periods, be it after a set number of trades or a specific time frame, and make data-driven decisions.
12. Iterative Improvements
The financial markets evolve, and so should your algorithm. Regularly review, analyze, and refine. Keep abreast with market news, economic events, and technological advancements to ensure your algorithm remains at its peak performance.
Embarking on the journey of algorithmic trading can seem daunting. For tailored solutions and expert guidance, reach out to Botix. We craft state-of-the-art trading algorithms, ensuring you stay ahead of the curve.